Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing the right printing method can make a significant difference in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and end-product quality. The two main types of thermal printing are Direct Thermal and Thermal Transfer, both of which have unique advantages and drawbacks. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of these printing methods, allowing you to determine which one aligns best with your specific needs.
Overview of Printing Methods
Thermal printing relies on heat to produce images and text on various substrates. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of the two primary thermal printing techniques can help businesses and individuals decide which method to implement.
What is Direct Thermal Printing?
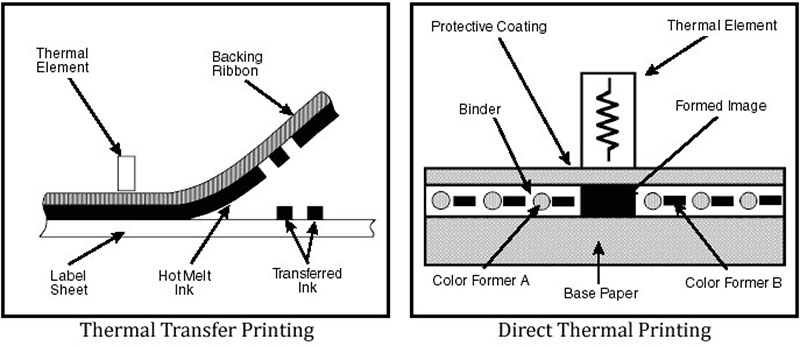
Direct Thermal Printing is a process that uses heat-sensitive paper. When the print head of the thermal printer applies heat, it interacts with a specially coated thermal paper, causing it to darken and create images or text. This printing method is commonly seen in applications such as receipts, labels, and barcodes because it is quick and requires minimal setup.
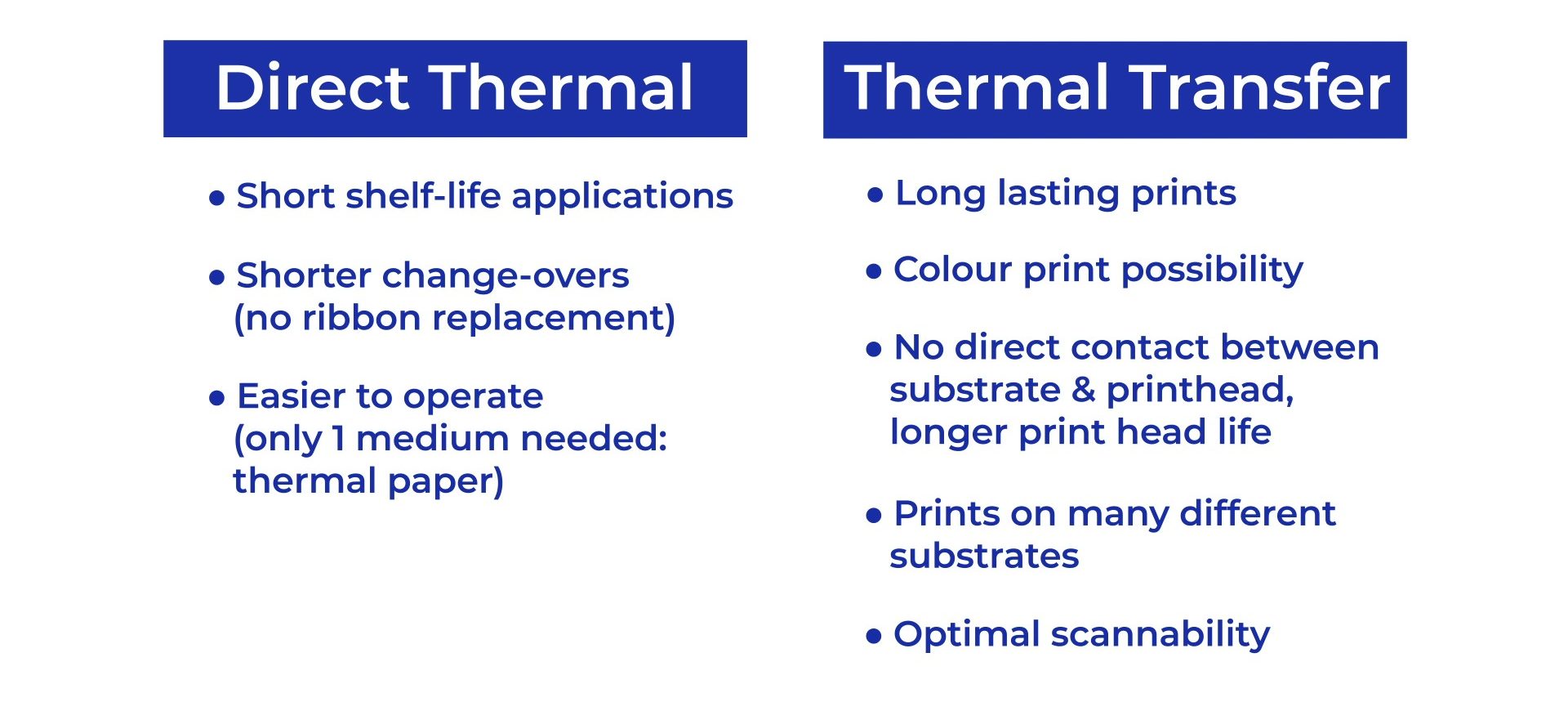
A primary advantage of direct thermal printing is its simplicity, as it eliminates the need for ink or toners, thus reducing maintenance and operational costs. However, one significant limitation is that prints can fade over time when exposed to heat, light, or abrasion, making them unsuitable for long-term archival usage or items that require durability.
The speed of direct thermal printing can range from a few inches per second to several inches per second, depending on the printer’s model and settings. According to industry studies, direct thermal printers can enhance workflow efficiency by producing clear and accurate prints in a matter of seconds, making them highly suitable for busy environments like retail locations and shipping departments.
What is Thermal Transfer Printing?
Thermal Transfer Printing, in contrast, employs a combination of heat and a ribbon coated with ink to produce images and text on labels or other substrates. In this method, the printer’s thermal print head melts the ink on the ribbon, which then transfers onto the selected surface. This approach is renowned for its ability to produce vibrant, high-resolution images and is often used where print longevity and quality are paramount.
Thermal transfer printing is versatile and can be used on various materials, including synthetic and paper substrates, making it ideal for applications such as product labeling, asset tracking, and shipping labels. The lifespan of these prints is significantly extended due to the robustness of the ink, which is resistant to scratches, moisture, and chemical exposure. Studies show that thermal transfer prints can last decades under optimal conditions, making them a preferred choice for industries that demand high durability.
Despite its advantages, thermal transfer printing may incur higher operational costs compared to direct thermal printing. Businesses must invest in ribbons and potentially more complex machinery that may demand more frequent maintenance. However, the investment is often justified by the superior quality and longevity of printed materials.
Key Differences
When comparing Direct Thermal and Thermal Transfer printing methods, various factors come into play, impacting the decision-making process based on the specific requirements of each application.
Durability and Longevity
The durability of prints is critical for various business needs. Direct thermal prints undergo a chemical reaction when heat is applied; however, this also means they are susceptible to fading over time, particularly when exposed to environmental factors such as sunlight or heat. For instance, a shipping label printed using direct thermal technology may become unreadable after a few months of outdoor exposure.
In contrast, thermal transfer prints boast enhanced durability. The ink, once transferred, bonds with the substrate, protecting it from scratches, smudges, and moisture. This enhanced longevity is essential for applications where labels must withstand harsh conditions, particularly in logistics and inventory management sectors, where products may face exposure to extreme temperatures or chemicals.
Print Quality
In terms of print quality, thermal transfer printing typically excels, producing sharper images and clearer barcodes that are crucial for accurate scanning processes. The ability to print at various resolutions allows businesses to customize their outputs to meet specific requirements. This is particularly beneficial in industries such as healthcare, where clear labels are necessary for medication tracking.
Conversely, while direct thermal prints can provide decent quality for less demanding tasks, they may not achieve the same level of sharpness or color vibrancy. Additionally, the reliance on thermal paper limits the versatility of textures and finishes available, confining its applications primarily to straightforward print jobs.
Cost Considerations
Cost is an essential factor when deciding between printing methods. Direct thermal printing generally has lower upfront costs since printers are less complex and do not require ribbons. However, long-term costs can accrue due to the need for frequent reprinting, particularly if labels become unreadable before their intended lifespan.
On the other hand, while thermal transfer printers may entail a higher initial investment owing to machinery and supplies, the quality and longevity of the prints can lead to savings over time. Businesses often find that fewer reprints and better durability offset the higher costs associated with thermal transfer methods. An analysis from industry reports suggests that companies can save between 20-30% in reprinting costs when opting for thermal transfer over time.
Applications for Each Method
Suitable Uses for Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing is ideally suited for scenarios where speed and convenience outweigh longevity and high-quality requirements. Its simplicity makes it a popular choice in various settings, including retail environments where high volumes of receipts are printed within a short period.
In the shipping and logistics sectors, direct thermal technology is frequently applied for generating labels for parcels and packages that are shipped daily. Its capacity to deliver quick prints makes it advantageous, particularly for businesses that prioritize efficiency and ease of use. Products labeled with direct thermal prints are often best used in controlled environments—such as indoor warehousing—where long-term durability is not vital.
Furthermore, event tickets or temporary passes that don’t need to endure the test of time can leverage direct thermal printing technology effectively. By utilizing direct thermal technology, organizations can streamline their processes and cut down costs on routine labeling without sacrificing essential functions.
Real-world examples include grocery store chains that widely use direct thermal printers for their POS systems to provide receipts instantly. Another example is shipping companies employing direct thermal printers to quickly print shipping labels, ensuring swift order fulfillment without the need for excessive materials or extensive setups.
In all these applications, direct thermal printing offers an actionable solution catering to industries with a high demand for rapid, simplistic printing processes, proving its utility in everyday operations.
Suitable Uses for Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing is highly versatile and suitable for a wide array of applications, primarily where durability and print quality are paramount. This method employs a heated ribbon to transfer ink onto the material, making it ideal for producing labels that must withstand harsh environments or be visually appealing.
One of the most common uses is in the production of labels for industrial purposes. For instance, in manufacturing and warehousing environments, labels must endure exposure to chemicals, abrasion, and extreme temperatures. The durability of thermal transfer prints ensures that critical information, such as safety warnings, handling instructions, and part numbers, remains legible throughout its lifecycle.
In the retail sector, thermal transfer printing is favored for producing high-quality barcodes and tags. Since these labels often require high resolution for scanning to be accurate, the clarity offered by thermal transfer prints is essential. Retailers particularly benefit from this technology when producing labels that display pricing information as well as promotional materials that need to be visually striking and appealing to consumers.
Food and beverage labeling is another sector where thermal transfer printing shines. Labels for perishable products must adhere to regulations that mandate clear expiry dates and nutritional information. These printed materials need to withstand condensation and potential spills without losing legibility. Thermal transfer prints, especially those made with resin-based ribbons, excel in these environments.
Finally, healthcare applications rely on thermal transfer printing for patient identification wristbands, laboratory specimen labels, and surgical instrument tags. The need for printing that is not only durable but also resistant to disinfectants and capable of remaining readable during the transport and storage of patient samples makes thermal transfer a critical choice in this field.
Pros and Cons Comparison
A thorough comparison of thermal transfer and direct thermal printing provides clarity on when to use each method. Below is an overview of the primary advantages and disadvantages of both techniques.
| Aspect | Thermal Transfer Printing | Direct Thermal Printing |
| Durability | High durability; resistant to elements | Less durable; sensitive to heat and light |
| Print Quality | High-resolution images & barcodes | Lower quality; best for simple texts |
| Label Variety | Compatible with a wide range of materials | Limited to thermal-sensitive materials |
| Operational Cost | Higher initial ribbon costs | Generally lower operating costs |
| Setup Time | Slightly longer due to ribbon installation | Quick setup with no ribbon required |
Advantages of Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing is characterized by its simplicity and efficiency. One of its significant advantages lies in its lower operational costs. Unlike thermal transfer printing, which necessitates the use of ink ribbons, direct thermal printing relies solely on thermal-sensitive media, which can decrease supply expenditures. Businesses can often find this method economically advantageous in high-volume printing scenarios, such as shipping labels, where low-cost labels can translate to higher profit margins.
Another advantage of direct thermal printing is the ease of use and lower maintenance involved. With fewer moving parts and no need to replace ribbons, users can enjoy reduced downtime and increased productivity. This is particularly beneficial in fast-paced environments where labeling needs can change rapidly, allowing for quick adaptations without significant resource input. Furthermore, with no additional consumables besides the label stock, this method simplifies inventory management.
A practical application of direct thermal printing can be seen in the logistics industry, where labels must be printed quickly and shipped out efficiently. Companies utilizing direct thermal printing can produce high volumes of shipping labels without worrying about the costs associated with ribbons, thus streamlining their operations effectively.
Advantages of Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing offers a range of beneficial features, particularly in regards to print quality and durability. One of the foremost advantages is the output quality. Since thermal transfer printing uses a ribbon to transfer ink onto the substrate, it produces sharper images and finer details compared to direct thermal printing. This results in clearer barcodes and more legible text, important for applications where precision is crucial, such as electronics and pharmaceuticals.
Durability is another hallmark of thermal transfer printing. The prints produced are typically resistant to scratching, smudging, and fading, making them ideal for environments exposed to elements that may otherwise ruin print quality. Labels created via this method can withstand high temperatures, chemicals, and moisture, which is vital in industries including manufacturing and healthcare.
Moreover, thermal transfer printing opens up a broader range of printable materials. Users can print on various substrates, including synthetic labels that provide enhanced durability or textured surfaces that are required in specialty applications. For example, in laboratory settings, researchers can utilize durable labels that endure rigorous cleaning and sterilization cycles without losing their readability, thus safeguarding critical information.
Disadvantages of Each Method
While both thermal transfer and direct thermal printing methods have their advantages, they also come with inherent disadvantages that warrant careful consideration.
For direct thermal printing, the primary drawback is the susceptibility of the printed labels to external conditions. Direct thermal prints can fade or deteriorate when exposed to heat and light over time, which can compromise the integrity of important information. This makes them less suitable for products subjected to long shelf lives or those needing clear information throughout their duration on the shelves.
Another challenge with direct thermal printing is its limited color capabilities. Since the method primarily uses thermal-sensitive color changes, it often produces black-and-white imprints or simple colors, which may not meet the aesthetic requirements of various branding needs.
On the other hand, thermal transfer printing has its challenges as well. One of the significant disadvantages is the ongoing cost associated with ink ribbons. While the print output quality is usually higher, the cost of ribbons can add up over time, especially with high-volume printing applications. Organizations need to factor this ongoing expense into their overall budget.
Additionally, the thermal transfer printing process can be slightly more complex, as it requires correct ribbon/label material pairings to achieve optimal results. Incorrect combinations can result in poor print quality or even damage to the printer itself, demanding more training for personnel involved in the printing process.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Choosing between direct thermal and thermal transfer printing ultimately depends on understanding specific operational needs and environmental factors associated with the intended applications.
Factors to Consider
When deciding on the printing method, several key factors should be evaluated. The first is the intended use of the printed labels. If the labels require exceptional durability and are intended for environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or varying temperatures is expected, thermal transfer printing may be the more appropriate choice. Conversely, if the labels will be used in short-term applications, such as shipping labels that will not endure long-term stress, direct thermal printing offers a cost-effective and efficient alternative.
The expected volume of printing also plays a crucial role. High-volume printing environments may benefit from thermal transfer printing because of the potential need for more resilient labels. However, if a company experiences fluctuations in printing needs, direct thermal printing provides added flexibility without the additional costs of purchasing ribbons.
Finally, consider the printing medium. If specific materials, like synthetic adhesive films or unique label stocks, are needed, thermal transfer printing has the widest application range.
Making the Decision
To make an informed decision, it is advisable to conduct a trial run of both printing methods in relevant scenarios. Testing each method’s effectiveness will provide insights into operational requirements, cost implications, and real-world challenges. Customer feedback enabling assessments of label performance can help clarify which method aligns better with organizational objectives and user expectations.
Collaboration with label and printer technology providers may also lead to optimized solutions tailored to specific needs, enhancing the decision-making process. Experts in the field can provide valuable insights into which method provides the most advantages for unique business applications.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
In summary, the choice between direct thermal and thermal transfer printing primarily depends on specific application requirements, durability needs, and economic considerations. Direct thermal printing is efficient for short-term, high-volume applications where cost-effectiveness comes to the forefront, while thermal transfer printing excels in scenarios demanding quality, durability, and versatility across various substrates.
By evaluating factors such as intended use, print volume, and material compatibility, businesses can make informed decisions that best fit their operational needs. Testing the technology in real-world applications and consulting with experts in the field can further refine this choice, ensuring optimal results. In an increasingly competitive market, the right printing method not only enhances efficiency but also elevates brand image and product integrity.
Final Recommendations
In the choice between direct thermal and thermal transfer printing, it is essential to evaluate your specific printing needs, application environments, and cost considerations. Both methods have their distinct advantages and considerations, making them suitable for different scenarios.
Firstly, direct thermal printing is ideal for short-term applications where labels or receipts do not require longevity. This method employs heat-sensitive paper that darkens when exposed to the print head. It’s commonly found in environments such as retail, where printing receipts or shipping labels is required. For instance, in high-volume retail settings, utilizing direct thermal printers can enhance efficiency because there are no ribbons to replace or ink cartridges to worry about. According to a survey by the National Retail Federation, retail environments are increasingly favoring direct thermal printing due to speed and cost efficiency, especially when the lifespan of printed materials is not a priority.
On the other hand, thermal transfer printing stands out for applications requiring durable and long-lasting prints. This technology involves melting resin from a ribbon onto the label material, creating a more robust print that withstands various environmental challenges like moisture or abrasion. For example, in manufacturing settings where labels need to endure harsh conditions, thermal transfer printers are frequently used. A case study from a logistics company highlighted that switching to thermal transfer labels significantly reduced replacement costs due to label failures, improving overall operational efficiency.
Additionally, potential users should consider the overall cost implications associated with each method. While direct thermal printers tend to have a lower initial purchase price and require minimal maintenance, the media costs can accumulate depending on volume. In contrast, thermal transfer printers have higher initial costs due to the need for ribbons, but the longevity of the labels can lead to reduced costs over time, especially for businesses that require labels to last longer than a few months.
Another critical aspect to consider is the scale and type of labeling needed. For businesses that require a diverse range of label sizes, shapes, and materials, investing in a thermal transfer printer may offer more versatility. Thermal transfer technology supports various materials, including synthetic labels that can be used in varied conditions, enhancing adaptability across various business functions.
Ultimately, an informed decision hinges on your operational needs, product turnover, environmental conditions, and print durability requirements. If your primary focus is on efficiency with a short lifespan, direct thermal is likely the best fit. Conversely, for applications necessitating durability and versatility, thermal transfer should be your go-to option.
In summary, understanding the unique characteristics of both direct thermal and thermal transfer printing methods is crucial in determining which printing technology aligns best with your operational goals. By evaluating your needs against the strengths and weaknesses of each method, you can ensure a well-informed choice that optimizes both functionality and cost-effectiveness in your labeling applications.